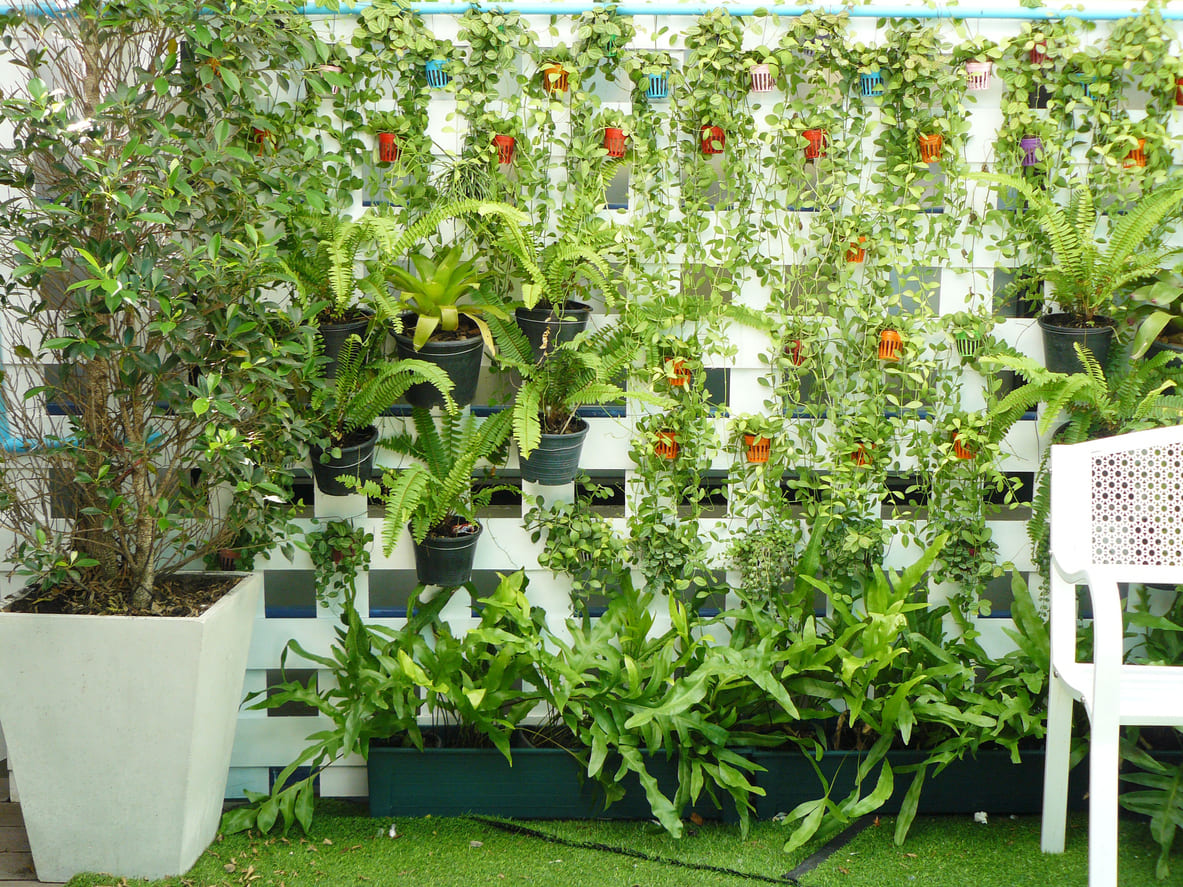
Gardening is a fantastic way to bring life and beauty to any space, but what if you don’t have much room? A vertical garden is the perfect solution. Whether you live in an apartment, have a small backyard, or simply want to maximize your available space, vertical gardens allow you to grow plants upwards instead of outwards. They are ideal for growing flowers, herbs, vegetables, and even small fruiting plants, adding greenery to walls, fences, balconies, or patios.
Creating a vertical garden is easier than you might think. With careful planning, the right plants, and some creativity, you can transform any wall or vertical surface into a lush, thriving garden. This step-by-step guide will help you design, build, and maintain a vertical garden that suits your space and needs.
Benefits of a Vertical Garden
Maximizes Space
One of the biggest advantages of a vertical garden is its ability to grow plants in limited areas. Whether indoors or outdoors, a vertical setup allows you to make the most of small spaces like balconies, patios, and even kitchen walls.
Improves Air Quality
Plants help filter pollutants and increase oxygen levels, improving indoor and outdoor air quality. A vertical garden can act as a natural air purifier, making your environment healthier.
Enhances Aesthetics
A well-designed vertical garden adds beauty and elegance to any space. Whether it’s a cascading wall of flowers or a structured arrangement of leafy greens, it creates a stunning focal point in homes, offices, or commercial spaces.
Reduces Heat and Noise
Plants provide natural insulation, helping regulate temperatures in both indoor and outdoor spaces. They can also help absorb sound, reducing noise pollution in urban areas.
Encourages Sustainability
Vertical gardens promote eco-friendly living by utilizing space efficiently, reducing soil erosion, and making gardening accessible to more people. They can also help conserve water when designed with smart irrigation systems.
Step 1: Choose the Location
Before you start building your vertical garden, decide where it will be placed. The success of your garden depends on selecting a location with the right conditions for plant growth.
Consider These Factors:
- Sunlight Exposure: Identify how much sunlight the space receives daily. Some plants thrive in full sun, while others prefer shade.
- Air Circulation: Ensure there’s enough airflow to keep plants healthy and prevent mold or mildew buildup.
- Water Access: Choose a spot with easy access to water for convenient irrigation.
- Structural Support: Walls, fences, railings, and trellises must be sturdy enough to support the weight of plants, soil, and containers.
Step 2: Select the Right Type of Vertical Garden
There are several ways to create a vertical garden, depending on your space, budget, and desired aesthetic.
1. Wall-Mounted Planters
These are excellent for small spaces and can be made from wooden pallets, fabric pockets, or modular panels. Wall-mounted systems work well for herbs, flowers, and small leafy greens.
2. Trellises and Climbing Supports
Ideal for vining plants such as tomatoes, peas, beans, and climbing roses. Trellises can be attached to walls, fences, or free-standing frames.
3. Hanging Pots and Baskets
Hanging planters work well for trailing plants like ferns, strawberries, and pothos. They add a decorative element while saving floor space.
4. Stackable Planters
Stacking pots or tiered plant stands create a layered effect, maximizing vertical space without attaching anything to walls.
5. Hydroponic or Aeroponic Systems
These systems use water and nutrients instead of soil, making them perfect for modern indoor gardens. They are highly efficient and great for growing herbs and leafy greens.
Step 3: Gather Materials and Tools
Depending on the type of vertical garden you choose, you’ll need different materials. Below is a general list of what you may need:
Materials:
- Wall-mounted planters, pallets, or fabric pockets
- Trellises or support structures
- Hanging baskets or stackable pots
- High-quality potting soil or hydroponic growing medium
- Plant seeds or seedlings
- Fertilizer (organic or slow-release)
- Irrigation system (drip irrigation, self-watering pots, or watering can)
Tools:
- Drill and screws (for wall-mounted systems)
- Hooks or brackets (for hanging baskets)
- Garden shears for pruning
- Watering can or hose
- Gloves for handling soil and plants
Step 4: Choose the Best Plants for Your Vertical Garden
Not all plants thrive in vertical gardens, so selecting the right ones is essential for success.
Best Plants for Vertical Gardens:
Herbs:
- Basil
- Mint
- Thyme
- Parsley
- Oregano
Vegetables:
- Cherry tomatoes
- Peppers
- Lettuce
- Spinach
- Beans (climbing varieties)
Flowers:
- Petunias
- Marigolds
- Begonias
- Fuchsias
- Climbing roses
Vining and Trailing Plants:
- Ivy
- Pothos
- Ferns
- Jasmine
- Passionflower
Consider the light and water needs of each plant before placing them in your vertical garden. Mixing plants with similar requirements ensures they thrive together.
Step 5: Assemble Your Vertical Garden
Once you’ve gathered all materials and selected your plants, it’s time to build your vertical garden.
- Install the Structure: Secure planters, trellises, or support frames to walls or fences using brackets and screws. Ensure they are stable and strong enough to hold plants.
- Prepare the Soil: Use high-quality potting mix that retains moisture but drains well. For hydroponic gardens, set up the water and nutrient system.
- Plant Strategically: Place taller or trailing plants at the top and smaller plants at the bottom to allow even sunlight distribution. Ensure plants have enough space to grow without overcrowding.
- Set Up Irrigation: Install a drip irrigation system or use self-watering pots to keep plants hydrated efficiently. If hand-watering, do so carefully to prevent overwatering.
Step 6: Maintain and Care for Your Vertical Garden
Watering:
Monitor moisture levels, as vertical gardens dry out faster than traditional gardens. Adjust watering based on plant needs and weather conditions.
Fertilizing:
Use organic compost or liquid fertilizers every few weeks to keep plants healthy. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth without strong roots.
Pruning and Harvesting:
Regularly trim plants to encourage growth and prevent overcrowding. Harvest herbs and vegetables frequently to promote continuous production.
Pest and Disease Control:
Check plants regularly for pests such as aphids and spider mites. Use natural pest control methods, like neem oil or introducing beneficial insects, to keep your garden healthy.
Final Thoughts: Transforming Your Space with a Vertical Garden
Creating a vertical garden is an excellent way to maximize your space while enjoying the beauty and benefits of plants. Whether you want a small herb garden in your kitchen, a lush green wall on your balcony, or a vibrant display of flowers on your patio, vertical gardening offers endless possibilities.
By selecting the right plants, setting up a sturdy structure, and maintaining your garden with proper care, you’ll have a thriving vertical garden that enhances your home’s atmosphere and promotes a sustainable lifestyle. Start planning today and experience the joy of growing upwards!