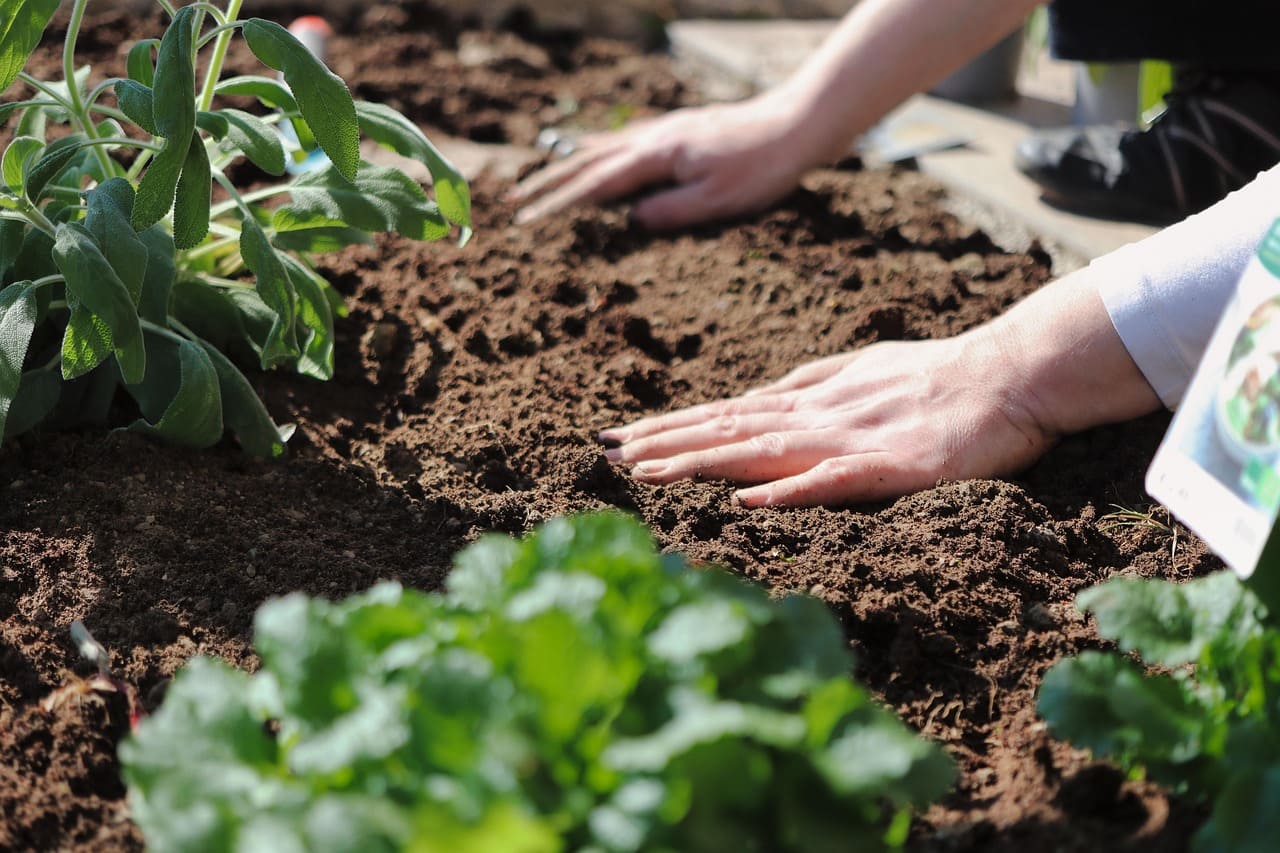
Growing your own vegetables at home is one of the most rewarding and sustainable ways to enjoy fresh, healthy produce. A home vegetable garden not only provides access to organic, pesticide-free food but also saves money and reduces reliance on store-bought produce. Whether you have a large backyard, a small patio, or just a few containers on a balcony, you can successfully grow a variety of vegetables with the right planning and care.
Starting a vegetable garden may seem overwhelming at first, but with proper guidance, anyone can cultivate a thriving and productive garden. This guide will walk you through every step, from selecting the right location and preparing the soil to planting, maintaining, and harvesting your vegetables.
Benefits of Growing Your Own Vegetables
1. Fresh and Nutritious Food
Homegrown vegetables are packed with flavor and nutrients, as they are harvested at peak ripeness without long storage or transportation periods.
2. Cost Savings
Growing your own vegetables can significantly reduce grocery bills. A single tomato plant, for example, can yield pounds of fresh tomatoes throughout the season.
3. Reduced Environmental Impact
A vegetable garden decreases dependence on store-bought produce, reducing plastic packaging and carbon emissions from transportation.
4. Gardening as a Stress Reliever
Gardening is a great way to relax, connect with nature, and relieve stress while also engaging in light physical activity.
5. Control Over Chemicals
When you grow your own food, you can choose organic fertilizers and natural pest control methods, ensuring that your vegetables are free from harmful chemicals.
Step 1: Choose the Right Location for Your Vegetable Garden
1. Sunlight Requirements
Most vegetables need at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight daily. Leafy greens like lettuce and spinach can tolerate partial shade, but sun-loving crops like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers require full sun.
2. Soil Quality
Rich, well-draining soil is essential for healthy plants. Conduct a soil test to determine pH levels and nutrient content. Vegetables generally prefer soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. If necessary, amend the soil with compost, aged manure, or organic matter to improve fertility.
3. Accessibility and Water Source
Choose a location near a water source for easy irrigation. Ensure the garden is accessible for regular maintenance, such as weeding, watering, and harvesting.
4. Protection from Pests and Wind
If possible, place your garden in a spot that is shielded from strong winds. Use fencing or raised beds to keep out animals like rabbits and deer.
Step 2: Decide on a Garden Type
Even with limited space, you can still grow a productive vegetable garden. Choose a method that works best for your available space and lifestyle.
1. Traditional In-Ground Garden
Best for larger yards, in-ground gardens allow plants to spread their roots naturally. Prepare the soil by removing weeds and tilling in compost for added nutrients.
2. Raised Beds
Raised garden beds provide better drainage, reduce weed growth, and make gardening more accessible. They are perfect for small spaces and areas with poor soil quality.
3. Container Gardening
If you have a balcony, patio, or small yard, container gardening is a great option. Use large pots, buckets, or grow bags to plant vegetables. Ensure containers have drainage holes to prevent root rot.
4. Vertical Gardening
For those with limited space, vertical gardening allows you to grow vegetables on walls, trellises, or hanging planters. Vining plants like cucumbers, beans, and tomatoes thrive in vertical gardens.
Step 3: Select the Best Vegetables for Beginners
If you’re new to gardening, start with easy-to-grow vegetables that require minimal maintenance.
Best Vegetables for Beginners
- Tomatoes – One of the most rewarding crops, tomatoes grow well in containers and raised beds.
- Lettuce – Fast-growing and perfect for continuous harvesting.
- Radishes – Ready to harvest in as little as 3-4 weeks.
- Carrots – Easy to grow in loose, well-draining soil.
- Zucchini – Produces abundant yields with minimal effort.
- Bell Peppers – Grow well in pots and need warm weather.
- Spinach – Thrives in cool weather and regrows after harvesting.
- Green Beans – Easy to grow and require minimal care.
Consider your local climate and growing season when selecting crops. Some vegetables, like tomatoes and peppers, thrive in warm weather, while others, like kale and lettuce, prefer cooler temperatures.
Step 4: Prepare the Soil and Plant Your Vegetables
1. Clear the Area
Remove weeds, grass, and debris from the planting area. If growing in raised beds or containers, fill them with high-quality potting mix and compost.
2. Add Organic Matter
Mix compost, aged manure, or organic fertilizer into the soil to boost nutrient levels. This enhances soil fertility and improves water retention.
3. Plant at the Right Time
Follow the recommended planting times for each vegetable. Some crops can be planted early in the season, while others should be started after the last frost.
4. Space Plants Properly
Overcrowding can lead to poor air circulation and increase the risk of disease. Check seed packets or plant labels for spacing guidelines to ensure each vegetable has enough room to grow.
Step 5: Watering and Maintaining Your Garden
1. Watering Tips
- Water deeply and consistently, especially during dry periods.
- Water in the early morning to minimize evaporation.
- Use a drip irrigation system or soaker hoses for efficient watering.
2. Mulching
Applying a layer of mulch around plants helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use organic materials like straw, wood chips, or grass clippings.
3. Weeding and Pruning
Regularly remove weeds that compete for nutrients and space. Prune excess foliage to improve air circulation and encourage healthy growth.
4. Fertilizing
Feed your plants with organic fertilizers like compost tea, fish emulsion, or slow-release granules. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive leaf growth with fewer fruits.
Step 6: Protect Your Garden from Pests and Diseases
1. Natural Pest Control
- Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs and praying mantises to control aphids and caterpillars.
- Plant marigolds, basil, or garlic to repel pests naturally.
- Use floating row covers to protect young plants from insects.
2. Common Diseases and Prevention
- Powdery Mildew: Improve air circulation and avoid overhead watering.
- Blight: Rotate crops each season to prevent disease buildup.
- Root Rot: Ensure proper drainage and avoid excessive watering.
Step 7: Harvesting Your Vegetables
Each vegetable has different harvesting times and techniques. Picking at peak ripeness ensures the best flavor and texture.
Harvesting Tips
- Leafy greens: Harvest outer leaves first to allow the plant to continue growing.
- Tomatoes and peppers: Pick when fully colored but still firm.
- Root vegetables: Pull up gently when they reach the desired size.
- Beans and peas: Harvest regularly to encourage continuous production.
Final Thoughts: Enjoy the Rewards of Home Gardening
Starting a vegetable garden at home is a fulfilling and rewarding experience that provides fresh, healthy food while connecting you with nature. With the right planning, soil preparation, and maintenance, even beginner gardeners can enjoy an abundant harvest.
By choosing easy-to-grow vegetables, following proper care techniques, and using natural pest control methods, you’ll set yourself up for a successful and sustainable garden. Whether you have a small space or a large backyard, a thriving vegetable garden is within your reach. Start planting today and experience the joy of growing your own food!